Exploring the World of FDM in Art Supplies, Product Design, and 3D Printing
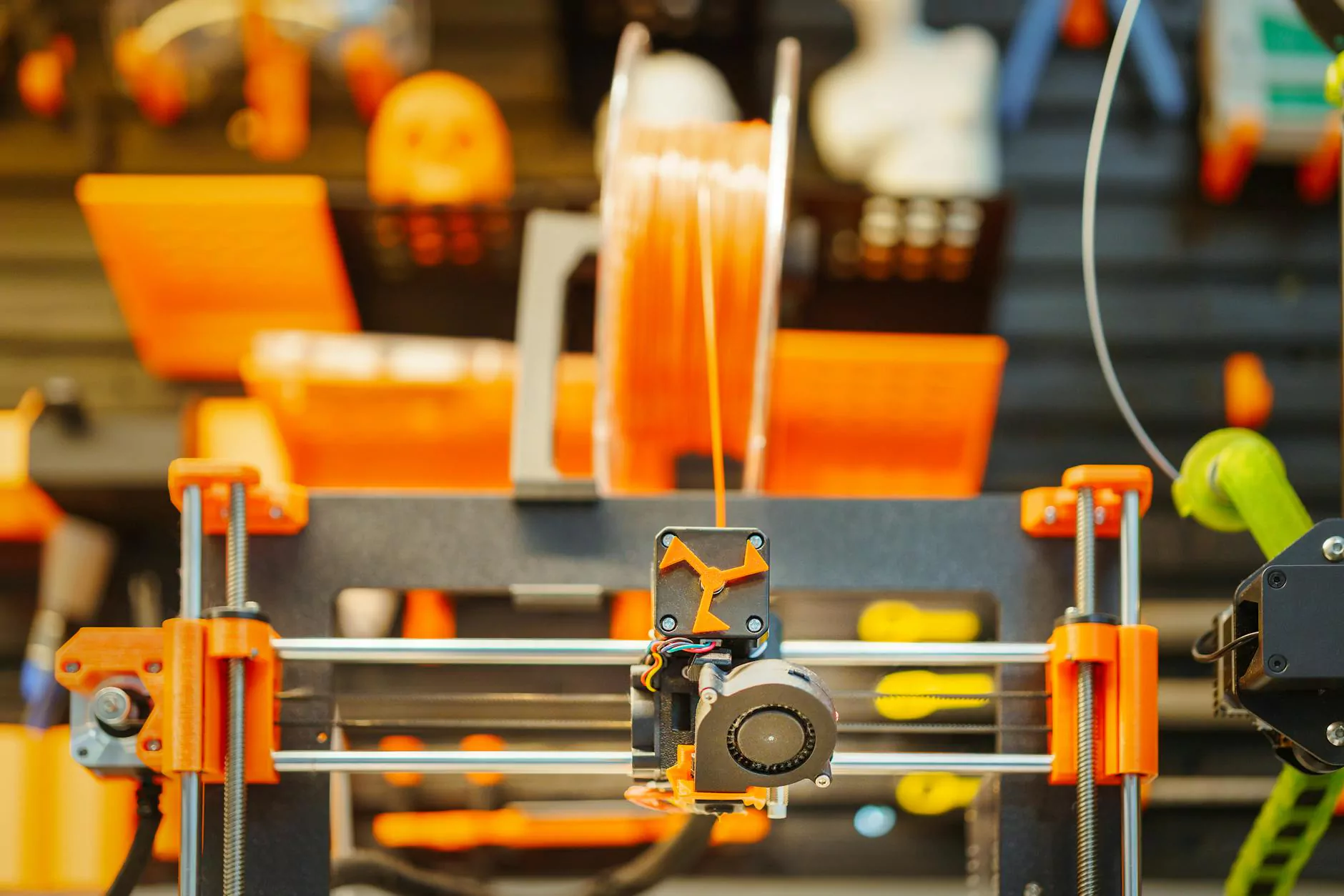

In recent years, the world of 3D printing has seen explosive growth and innovation, particularly with the advent of Fused Deposition Modeling, commonly referred to as FDM. This revolutionary technology is reshaping various industries, particularly in the realms of art supplies, product design, and 3D printing. This article delves deep into how FDM is transforming these fields and what it means for the future of creativity and manufacturing.
Understanding FDM Technology
FDM is a popular 3D printing technology that works by melting and extruding thermoplastic filament through a heated nozzle to create parts layer by layer. This process enables the production of complex geometries and customized designs, making it a favorite among artists, designers, and engineers alike.
The Mechanics of FDM
The FDM process involves several steps:
- Filament Loading: The thermoplastic filament is fed into the printer.
- Heating: The nozzle heats up to the melting point of the filament.
- Extrusion: The melted filament is extruded through the nozzle onto the build platform.
- Layering: Each layer is deposited in succession until the entire model is complete.
- Cooling: The material solidifies, creating a durable part.
Materials Used in FDM
FDM printers work with a variety of thermoplastics, including:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): Biodegradable and easy to print, ideal for beginners.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Strong and durable, suitable for functional prototypes.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Offers a good balance of strength and flexibility.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): A flexible filament perfect for creating rubber-like parts.
The Impact of FDM on Art Supplies
For artists, FDM technology opens up a vast array of possibilities. Traditional art supplies have traditionally been somewhat limited in scope, but with the emergence of 3D printing, creativity knows no bounds.
Creating Custom Art Supplies
Artists can now create customized tools tailored to their unique styles and preferences. For instance:
- Custom Brushes: Artists can design brushes specifically suited to their techniques.
- Unique Palettes: 3D-printed palettes can include sections designed for specific colors and mediums.
- Personalized Sculpting Tools: Tools can be shaped for better ergonomics and functionality.
Prototyping Art Pieces
FDM allows artists to create rapid prototypes of their works. This is particularly useful in the world of sculpture and installation art.
- Scale Models: Artists can create small-scale models before committing to full-sized pieces.
- Experimentation: The ability to produce multiple iterations quickly allows for more experimental workflows.
Innovations in Product Design Using FDM
In the field of product design, FDM has become an invaluable tool. It bridges the gap between innovation and practical application through fast prototyping and production.
Rapid Prototyping
Traditional prototyping methods can be time-consuming and expensive. FDM technology enables designers to:
- Reduce Lead Times: Prototypes can be printed in a matter of hours rather than weeks.
- Lower Costs: Printing a prototype is significantly less expensive than manufacturing via traditional methods.
- Iterate Designs Quickly: Designers can quickly modify and reprint models to refine their concepts.
Design Customization
FDM also allows for high levels of customization:
- Consumer-Centric Designs: Products can be tailored to meet specific user needs and preferences.
- Unique Aesthetic Features: Designers can experiment with intricate designs and shapes that would be impossible to achieve through conventional manufacturing processes.
The Future of FDM in 3D Printing
As technology continues to advance, the potential applications of FDM in 3D printing are expanding exponentially.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Printing
Sustainability is a growing concern across industries, and FDM technology is no exception. There are emerging eco-friendly materials that can be used in FDM printing:
- Recycled Plastics: Using recycled materials can greatly reduce environmental impact.
- Biodegradable Polymers: Materials like PLA are derived from renewable resources and are compostable.
Integration with Other Technologies
The future holds exciting possibilities for FDM integration with other technologies, such as:
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies can enhance design processes and optimize manufacturing.
- IoT and Smart Manufacturing: Connecting printers and materials to the internet could streamline production and improve quality control.
Conclusion
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is revolutionizing industries by merging art and technology, enabling designers and artists to bring their visions to life with unprecedented ease and creativity. From custom art supplies to advanced product design, FDM is not just a passing trend but a long-lasting change in how we approach manufacturing and creativity.
As we look to the future, the integration of sustainable practices and new technologies will make FDM an even more powerful tool for innovation. At Arti90.com, we are excited to explore these advancements and support our creative community in leveraging FDM technology to its fullest potential.